2. 中国地震局地震预测研究所, 北京 100036
2. Institute of Earthquake Science, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing 100036, China
加卸载响应比理论(LURR)[1-6]是预测地震的新方法,把介质加载响应与卸载响应的比值定义为加卸载响应比.对于地球介质,日月运行产生的引潮力为它提供了天然的加卸载手段.我们以贝尼奥夫应变作为响应量确定孕震区的加卸载响应比演化过程,刻画震源区介质的损伤程度,反映地震孕育的进程,从而预测地震.它自20世纪80年代提出,至今已近30年,在这期间很多人对加卸载响应比做了大量基础研究,包括物理机制、实验研究和数值模拟,并取得了一系列新的进展[7-17].在地震预测实践中加卸载响应比取得了一定的效果,异常区与地震发生的位置有较好的对应性[18-20],但是总的来说,预测效果仍不尽如人意.究其原因主要在于,在实际预测中与当地的地球物理条件结合得不够.例如,本课题组通过统计研究得到了发震时间与震级(M≥5)的函数关系式[21].在新疆地区应用此结果发现,该地区的实际发震时间远小于根据公式算出的时间.导致这一结果的原因是新疆地区构造运动剧烈,剪切应变率较大.这说明特征时间不只是震级的函数,还与当地的地质构造有关,所以地震预测一定要与当地的实际情况结合.
量纲分析综合考虑诸多因素对地震的影响.而今,“量纲分析在科学和技术的各个分支的基础理论和实际问题中得到广泛的应用,它是分析和研究问题的有力手段和方法,是探讨科学规律,解决科学和工程问题的有效工具"[22-24].本文尝试将量纲分析与加卸载响应比结合应用于地震预测.
地震预测是根据我们对地震规律的认识,预测未来地震发生的地点、强度和时间.这三点也是地震预测面临的三大难题.文中采用量纲分析与加卸载响应比相结合的方法,选用自1970年以来发生在中国大陆的34个地震资料(见表 1),讨论如何对未来地震发生的地点、强度和时间进行判断.
|
|
表 1 选用的地震 Table 1 The earthquakes used in the paper |
地震预测必须预测未来地震发生的时间、地点和强度,这三点也是地震预测的三要素,简称时、空、强.以下分别讨论.根据量纲分析与加卸载响应比相结合的分析过程,首先判断地震发生的地点.
2.1 预测未来地震发生的地点20年来,我们连续对中国大陆进行LURR 的近实时的时空扫描.结果表明,发生在资料较好地区的地震大都落在LURR 的异常区内[12].所以,可以根据LURR 异常区预测未来地震发生的地点.为了规范加卸载响应比扫描时的参数,便于对不同时段、地区和研究者的结果进行比较,我们规范了加卸载响应比扫描的固定的扫描半径及对应的时间段,如扫描半径为200km 对应的时间段是18个月.文中使用的震例,根据加卸载响应比的演化结果选取孕震区,观察并选取对应地震异常区面积最大的区域.对于未发生地震,且资料充足地区,若某一异常区稳定存在,并呈现典型的演化规律(加卸载响应比由小变大,达到峰值后再变小),可以初步判定该地区有可能发生地震,并选取异常区面积最大的区域,根据该地区的地球物理参数,通过量纲分析与LURR 的结合,对地震强度和发震时间做进一步的判断.
2.2 预测未来地震的强度地震的强度通常用震级M来表示,它是通过地震释放的地震波能量Es 来衡量的.影响地震能量释放的因素很多,那么量纲分析中的变量该如何选取呢?从能量平衡这一基本物理角度出发,考虑到资料获得的可能性,我们选取了如下变量:Ew,Ipp,$\dot \gamma $ ,h,认为它们和震级有关.
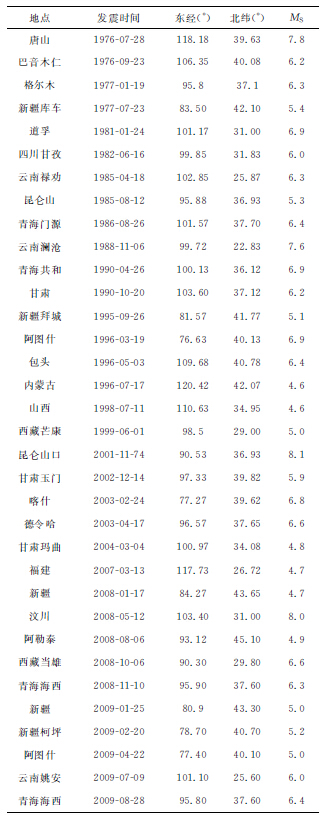
Ew:某一地区地震活动性的定量表征.Ew 等于该地区长时期(T)里所有地震辐射的地震波能量总和,除以T和其面积,单位是J/(km2·s-1).从能量平衡的角度看,它也和该地区长时间里由于构造运动积累的能量(应变能)有关.我们用1900 年到2009年这110年的地震目录,计算了地震波辐射的总能量,再除以时间和面积就得到中国大陆各地单位时间和面积释放的平均地震波能量Ew.中国大陆各地Ew 的分布见图 1.
|
图 1 中国陆地各地平均地震波能量Ew 的分布图 Fig. 1 The distribution of the average seismic wave energy in Chinese Mainland |
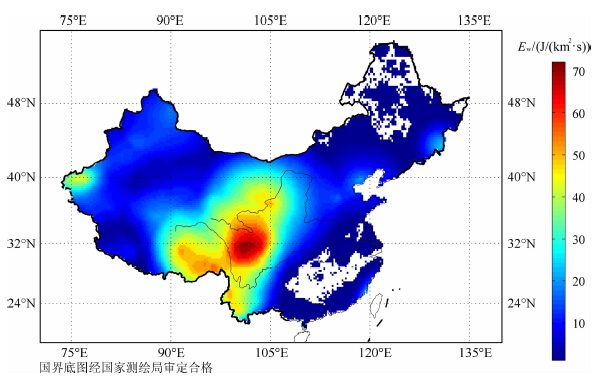
Ipp:首先定义面积分It为:
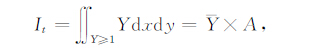
|
(1) |
It是随时间变化的,它是孕震区的面积A和LURR的平均值Y 的乘积,综合地表征了孕震区的大小和程度,单位km2.
Ipp是It的最大值.图 2是汶川地震(2008)异常区的It变化和地震时序(通常称为M-T图).
|
图 2 汶川地震(2008)异常区的It和地震时序 Fig. 2 It and the earthquake sequence in the seismogenic zone of Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 |
$\dot \gamma $ :某一地区的剪切应变率,单位是10-9rad/a.某一地区的剪切应变率表征该地区的构造运动的剪应力加载率(二者只差一个弹性常数,但应变率便于测量).本文主要采用沈正康等[25]用GPS 测量得到的结果,同时参照顾国华[26]的结果.
h:孕震区的厚度,单位km.令V=A×h,可以将V看作孕震区的体积.
根据以上参数做量纲分析如下:
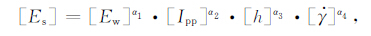
|
(2) |
本文选取时间(T),长度(L)和力(F)作为基本量纲,把(2)式写成量纲的形式为:
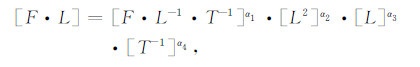
|
(3) |
令β =h/$\sqrt A $,最后得出:
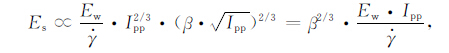
|
(4) |
由(4)式可以得到:
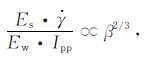
|
(5) |
显然(5)式左边和右边都是无量纲量,由此得到无量纲数
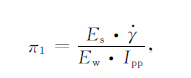
|
(6) |
若令
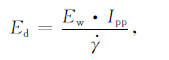
|
(7) |
则
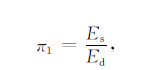
|
(8) |
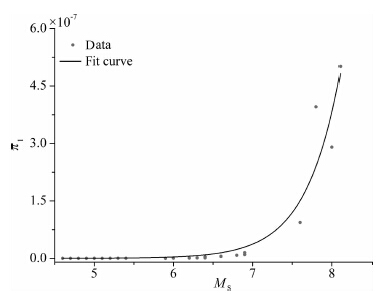
π1 是震级的函数,即π1=f(M),通过excel拟合曲线,R2=0.96(R2是拟合曲线中自变量和因变量的相关系数,越接近1说明自变量和因变量越相关,曲线拟合得越好),见图 3.
|
图 3 π1 与震级的关系 Fig. 3 The relation between π1 and the magnitude of earthquake |
最后得到数学关系式:
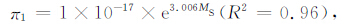
|
(9) |
由上式反推出的震级记为Ms1,
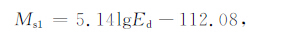
|
(10) |
把经过数据处理后的结果记为Msp:
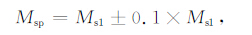
|
(11) |
上式中误差项的系数0.1[23]是经过数据处理后确定的.Msp即为预测未来发生地震的震级.
2.3 预测未来地震的发震时间把It函数的峰值点Ipp所对应的时间记为Tpp,峰值点过后地震发生,Tpp与地震发生的时间间隔记为T2.显然与时间相关的量是T2 和剪切应变率.通过量纲分析得到无量纲数π2:
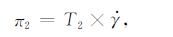
|
(12) |
特征时间T2 也与发震震级、当地的平均地震波能量和Ipp相关,令π1 与π2 相乘可以得到无量纲数π3:
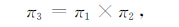
|
(13) |
π3 是π1 和π2 的函数,也是震级的函数,即π3 =f(π1,π2)=f(M),通过excel拟合曲线可以得到π3 与震级的关系,R2=0.94,见图 4.
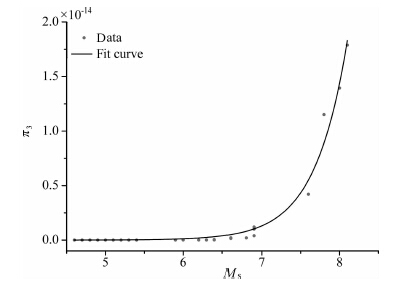
|
图 4 π3 与震级之间的关系 Fig. 4 The relation between π3 and the magnitude |
π3 与震级的数学关系式为:
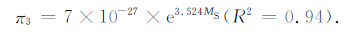
|
(14) |
由上式反推出的特征时间记为T21:
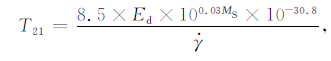
|
(15) |
把经过数据处理后的结果记为T2p:
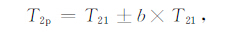
|
(16) |
b是数据处理后的误差项系数,若预测未来地震发生的震级在4.5~5.5 内,b=0.1[15];震级在5.6~6.5内,b=0.27;若震级大于等于6.6,则b=0.3.T2p的单位是月,代表预测未来地震的Tpp与地震发生的时间间隔.
3 分析结果对已有震例的验证以上分析结果是通过对文中选用的34个震例进行统计研究得到的.此结果对已发生的地震有较好的验证性.下面以汶川地震(2008)和河南周口地震(2010)为例说明.
3.1 汶川地震(2008)2008年5 月12 日汶川发生8.0 级地震,震中(北纬31.0°,东经103.4°).
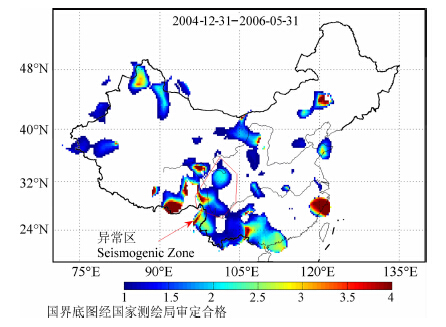
首先根据LURR 时空扫描选取异常区,见图 5中红色线选中的区域,异常区内It值和地震时序见图 2.在异常区内确定地球物理参数并由量纲分析结果反推出震级Msp=7.9±0.8,特征时间T2p为28±9(月).Tpp所处的时间是2005 年10 月,所以“预测"地震发生的时间为2008年2月(±9个月),实际地震发生于2008年5月,在“预测"的时段内.
|
图 5 汶川地震(2008)加卸载响应比异常区 (图中红色连线包围的区域) Fig. 5 The seismogenic zone of Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 (the zone encircled by red contour) |
2010年10月24日河南周口发生4.7级地震,震中(北纬34.1°,东经114.6°).
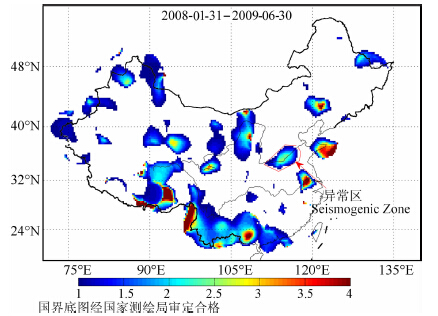
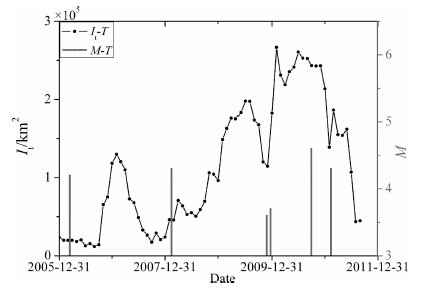
选取异常区如红色线包围区域(见图 6),此区域内It及地震时序见图 7.在异常区内确定地球物理参数并根据文中的分析结果得出Msp=4.4±0.5,T2p=11±2(月).Tpp所处的时间是2010年1月,所以“预测"地震发生的时间是2010 年10 月-2011年2月,在“预测"范围内.
|
图 6 河南周口地震异常区 (图中红色连线包围的区域) Fig. 6 The seismogenic zone of Zhoukou earthquake (the zone encircled by red contour) |
|
图 7 周口地震异常区的I(t)变化及地震时序 Fig. 7 I(t) and the earthquake sequence in the seismogenic zone of Zhoukou earthquake |
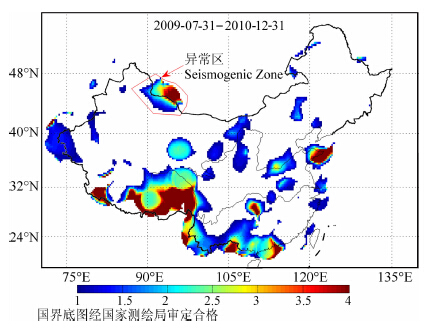
通过量纲分析与加卸载响应比相结合的方法得出无量纲数是为了探索地震发生的规律,最终目的是应用于地震预测实践.根据LURR 的时空扫描结果,在新疆阿勒泰地区选取异常区(见图 8),尝试使用本文的分析结果预测未来地震发生的地点、强度和时间.
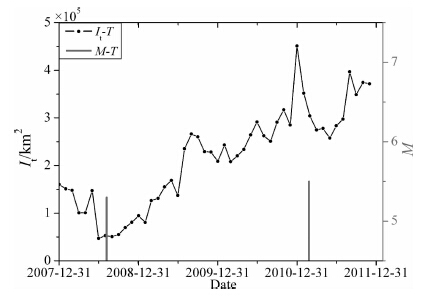
异常区的It及近年来地震时序见图 9,确定异常区的地球物理参数,根据量纲分析结果得出未来发生地震的震级Msp=5.5±0.5,特征时间T2p为17±2(月).Tpp所处的时间为2010年12月,由此可以得出未来地震发生的时间为2012年3月-7月.
|
图 8 阿勒泰异常区选取 (图中红色连线包围的区域) Fig. 8 The seismogenic zone of Altay (the zone encircled by red contour) |
|
图 9 阿勒泰地区异常区内It变化及地震时序 Fig. 9 It and the earthquake sequence in the seismogenic zone in Altay |
本文把量纲分析与加卸载响应比结合应用于地震预测,得到了均与震级成指数关系的无量纲数π1和π3,此结果对已经发生的地震有较好的验证性,而我们的最终目的是应用于地震预测.在判断未来地震发生的地点、强度和时间时,首先要根据LURR 扫描结果确定出孕震区域;然后确定孕震区的地球物理参数Ew,Ipp和$\dot \gamma $ ,计算出Ed,根据公式(10)和(11)得出未来地震的震级Msp;最后由公式(15)和(16)得出特征时间T2p,Tpp+T2p的结果就是未来地震发生的时间.
以上工作是基于基础科学框架而建立的.分析过程中对参数的选用非常重要,由于地球内部的不可深入性,导致很多变量无法获得,或重要变量获得的不完整.例如岩石的强度、弹性模量和断裂韧度等,都是非常重的变量,一般通过实验来获得,但是地下几十千米介质的这些参数我们难以得知;而就广度而言,不同地区介质的性质也不同,应用起来非常困难.考虑到资料的可获得性,本文使用了Ew,Ipp,$\dot \gamma $ ,h,但是对选用数据的质量有了很大限制.
在质上,例如剪切应变率的选取,若能使用孕震时段的数据则更为合理,由于各种限制,本文使用了1991-2000年的结果[25-26];在量上,对不同地区应该按时间顺序选用多个地震,限于部分地区资料无法获得以及时间关系,只选用了自1970 年以来的34个地震数据,数量上欠少.
本文初步尝试把量纲分析应用于地球科学,目前只是初步研究,随着科技的进步,变量获得的完整性与可使用性提高,我们还会继续改进.
致谢文中使用的形变数据由沈正康教授、江在森研究员和顾国华研究员提供,地震目录来自于中国地震台网中心,部分计算是在中国科学院超级计算中心完成的,在此一并表示感谢.
| [1] | 尹祥础. 地震预测新途径的探索. 中国地震 , 1987, 3(1): 1–7. Yin X C. The new approach of earthquake prediction. Earthquake Research in China (in Chinese) , 1987, 3(1): 1-7. |
| [2] | 尹祥础, 尹灿. 非线性系统失稳的前兆与地震预报——响应比理论及其应用. 中国科学B辑 , 1991, 21(5): 512–518. Yin X C, Yin C. The precursor of instability for nonlinear system and earthquake prediction—load/unload response ratio theory and its application. J. Science in China (Series B) (in Chinese) , 1991, 21(5): 512-518. |
| [3] | 尹祥础, 陈学忠, 尹灿. 加卸载响应比——一个刻划构造运动稳定性的新参数及其在地质灾害预测中的应用. 地球物理学进展 , 1993, 8(4): 90–96. Yin X C, Chen X Z, Yin C. Loading and unloading response ratio——a new parameter determing the degree of stability of tectonic movement and its application to prediction of geological disasters. Progress in Geophysics (in Chinese) , 1993, 8(4): 90-96. |
| [4] | 尹祥础, 陈学忠, 宋治平, 等. 加卸载响应比─一种新的地震预报方法. 地球物理学报 , 1994, 37(6): 767–775. Yin X C, Chen X Z, Song Z P, et al. The load-unload response ratio theory: a new approach to earthquake prediction. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 1994, 37(6): 767-775. |
| [5] | Yin X C, Chen X Z, Song Z P. The load/unload response ratio (LURR) theory and its application to earthquake prediction. Journal of Earthquake Prediction Research , 1994, 3(3): 325-333. |
| [6] | Yin X C, Chen X Z, Song Z P, et al. A new approach to earthquake prediction—the load/unload response ratio (LURR) theory. Pure Applies Geophysiscs , 1995, 145(3-4): 701-715. DOI:10.1007/BF00879596 |
| [7] | 施行觉, 许和明, 万永中, 等. 模拟引潮力作用下的岩石破裂特征─加卸载响应比理论的实验研究. 地球物理学报 , 1994, 37(5): 633–637. Shi X J, Xu H M, Wan Y Z, et al. The characteristic of rock fracture under simulated tide force─laboratory study on the theory of loading and unloading response ratio. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 1994, 37(5): 633-637. |
| [8] | 尹祥础, 陈学忠, 宋治平. 加卸载响应比理论及其在地震预测中的应用研究进展. 地球物理学报 , 1994, 37(S1): 223–230. Yin X C, Chen X Z, Song Z P. The development of load-unload response ratio theory and its application to earthquake prediction. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 1994, 37(S1): 223-230. |
| [9] | 施行觉, 卢振刚, 许和明. 岩石非线性破裂的衰减特征. 地球物理学报 , 1996, 39(S1): 231–237. Shi X J, Lu Z G, Xu H M. The attenuation characteristic of rock's non-linear fracture. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 1996, 39(S1): 231-237. |
| [10] | 王裕仓, 尹祥础, 彭克银, 等. 加卸载响应比的数值模拟. 地球物理学报 , 1999, 42(5): 669–676. Wang Y C, Yin X C, Peng K Y, et al. Numerical simulation on load/unload response ratio theory. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese) , 1999, 42(5): 669-676. |
| [11] | Yin X C, Chen X Z, Wang Y C, et al. Development of a new approach to earthquake prediction—load/unload response ratio (LURR) theory. Pure and Applies Geophysiscs , 2000, 157(11-12): 2365-2383. |
| [12] | Yin X C, Mora P, Peng K Y, et al. Load-unload response ratio and accelerating moment/energy release critical region scaling and earthquake prediction. Pure and Applied Geophysics , 2002, 159(10): 2511-2523. DOI:10.1007/s00024-002-8745-4 |
| [13] | Yu H Z, Cheng J, Zhu Q Y, et al. Critical sensitivity of load/unload response ratio and stress accumulation before large earthquakes: example of the 2008 Mw7.9 Wenchuan earthquake. Natural Hazards , 2011, 58(1): 251-267. DOI:10.1007/s11069-010-9664-9 |
| [14] | Yu H Z, Zhu Q Y. A probabilistic approach for earthquake potential evaluation based on the Load/Unload Response ratio method. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience , 2010, 22(12): 1520-1533. |
| [15] | Yin X C, Zhang L P, Zhang H H, et al. LURR's twenty years and its perspective. Pure and Applied Geophysics , 2006, 163(11-12): 2317-2341. DOI:10.1007/s00024-006-0135-x |
| [16] | 张浪平, 余怀忠, 尹祥础, 等. 加卸载响应比方法在结构灾变预测中的应用. 工程力学 , 2010, 27(3): 228–235. Zhang L P, Yu H Z, Yin X C, et al. Application of the load/unload response ratio method in catastrophic failure prediction of structures. Engineering Mechanics (in Chinese) , 2010, 27(3): 228-235. |
| [17] | Zhang H H, Yin X C, Liang N G, et al. Acoustic emission experiments of rock failure under load simulating the hypocenter condition. Pure and Applied Geophysics , 2006, 163(11-12): 2389-2406. DOI:10.1007/s00024-006-0129-8 |
| [18] | 尹祥础, 陈学忠, 宋治平, 等. 关东等地区加卸载响应比的时间变化及其预测意义. 中国地震 , 1996, 12(3): 331–334. Yin X C, Chen X Z, Song Z P, et al. The temporal variation of LURR in Kanto and other regions in Japan and its application to the earthquake prediction. Earthquake Research in China (in Chinese) , 1996, 12(3): 331-334. |
| [19] | 宋治平, 尹祥础, 王裕仓, 等. 美国加州地区地震前加卸载响应比的时空演化特征及预测意义. 地震学报 , 2000, 22(6): 588–595. Song Z P, Yin X C, Wang Y C, et al. The tempo-spatial evolution characteristics of the load/unload response ratio before strong earthquakes in California of America and its predicting implications. Acta Seismological Sinica (in Chinese) , 2000, 22(6): 588-595. |
| [20] | 尹祥础, 张浪平, 张永仙等. 大地震前LURR的大时空异常—预测中国大陆未来大地震的探讨. //中国大陆强震趋势预测研究(2009年度). 北京: 地震出版社, 2008: 144-150. Yin X C, Zhang L P, Zhang Y X, et al. LURR anomoly with great tempo-spatial scale before large Earthquake—Prediction of the upcoming great earthquake in the Chinese mainland. // The Researches on Prediction of the Strong Earthquake Tendency for Chinese Mainland in 2009 (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press, 2008: 144-150. |
| [21] | 张晖辉, 尹祥础, 梁乃刚. 中国大陆地区中强地震前加卸载响应比异常时间尺度的统计研究. 中国地震 , 2005, 21(4): 486–495. Zhang H H, Yin X C, Liang N G. Statistic study of LURR anomaly temporal scale before moderately strong earthquakes on the Chinese mainland. Earthquake Research in China (in Chinese) , 2005, 21(4): 486-495. |
| [22] | Sedov L I. Similarity and Dimensional Methods in Mechanics. London: Academic Press, 1959 . |
| [23] | 钱伟长. 应用数学. 安徽: 科学技术出版社, 1993 . Qian W C. Applied Mathematics (in Cinese) (in Chinese). Anhui: Science and Technology Press, 1993 . |
| [24] | 谈庆明. 量纲分析. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2007. Tan Q M. Dimensional analysis (in Cinese). Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2007. http://www.oalib.com/references/16173008 |
| [25] | 沈正康, 王敏, 甘卫军, 等. 中国大陆现今构造应变率场及其动力学成因研究. 地学前缘 , 2003, 10(特刊): 93–100. Shen Z K, Wang M, Gan W J, et al. Contemporary tectonic strain rate field of Chinese continent and its geodynamic implications. Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese) , 2003, 10(特刊): 93-100. |
| [26] | Gu G H, Shen X H, Wang M, et al. General characteristics of the recent horizontal crustal movement in Chinese mainland. Acta Seismological Sinica , 2001, 23(4): 362-369. |
 2012, Vol. 55
2012, Vol. 55